
Recently, Lu Lan’s research team from the School of Pharmacy of Chengdu University (CDU) published a highly cited review paper in a top international pharmacy journal, with CDU as the first author's affiliation and researcher Lu Lan as the first author and corresponding author. The paper is entitled "Screening strategies for quorum sensing inhibitors in combating bacterial infections", which is published in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis (2022 Top Journals of Pharmacy Q1 by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, IF: 14.026).
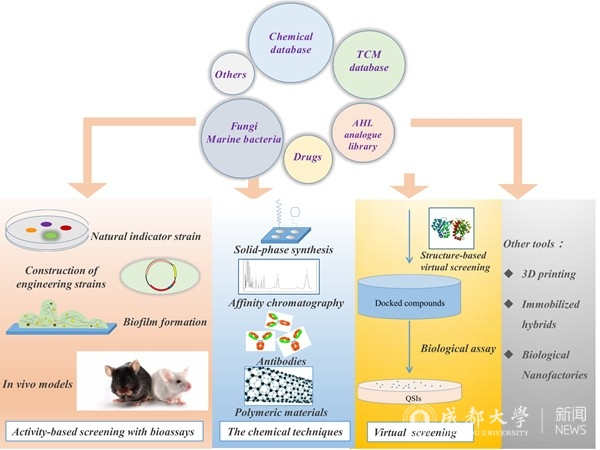
Interference with quorum sensing (QS) represents an antivirulence strategy for the inhibition of bacterial virulence factors rather than the bacteria themselves. Bacterial virulence factors are usually not necessary elements for bacterial growth, so the selective pressures of bacteria are small, and difficult to develop drug resistance. The quorum quenching approaches and the discovery of quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs) have a strong impact on the discovery of anti-infective drugs against various types of bacteria. There are diverse approaches for the discovery of QSIs. This review highlights the latest findings in strategies and methodologies for QSI screening, involving activity-based screening with bioassays, chemical methods to seek bacterial QS pathways for QSI discovery, virtual screening for QSI screening, and other potential tools for interpreting QS signaling, which are innovative routes for future efforts to discover additional QSIs to combat bacterial infections.
In addition, another review paper “Developing natural products as potential anti-biofilm agents” delivered by Lu Lan's research team has also attracted higher attention (published in 2019,127 Citations, data source: Web of Science). This paper introduced the important application of natural small molecules and traditional Chinese medicine in the anti-infective therapy of virulence factors such as antibacterial biofilm.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2021.03.009
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-019-0232-2