Recently, faculty and students from the School of Pharmacy and the Sichuan Industrial Institute of Antibiotics of Chengdu University published a research paper titled "Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases from the Akkermansia Genus" in the International Journal of Food Microbiology (top journal among the Tier 1 of the Chinese Academy of Sciences). Lin Jiafu, an associate researcher in the Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy, and Wang Tiantian, a graduate student from the Class of 2022 in the School of Pharmacy, are co-first authors. Associate Researcher Song Tao serves as the corresponding author, and Chengdu University is listed as the affiliated institution for both the first author and the corresponding unit.

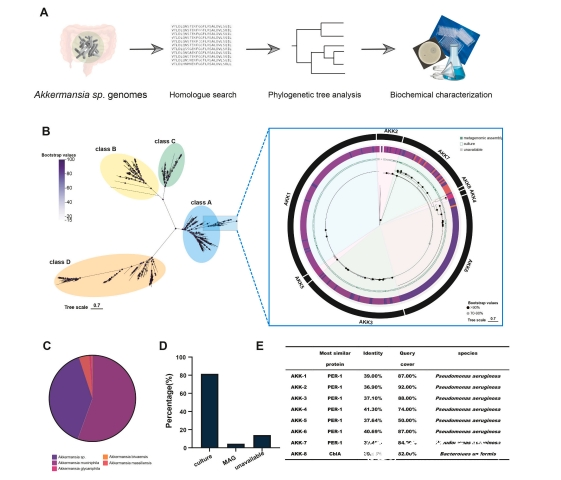
β-lactam antibiotics possess broad-spectrum and highly effective antibacterial activity, making them widely used in clinical treatments. The extensive use and misuse of β-lactam antibiotics have led to the rapid spread of β-lactam-resistant bacteria, becoming a significant global public health issue. In this paper, 8 novel β-lactamase genes were successfully identified and characterized from the genome of Akkermansia muciniphila, exhibiting only 36.90% to 41.30% sequence similarity with known genes. This represents the first molecular identification and functional validation of β-lactamases derived from the Verrucomicrobia phylum. Akkermansia-derived β-lactamases can hydrolyze penicillins, cephalosporins, and monocyclic β-lactam antibiotics. It is worth mentioning that the Akkermansia-derived β-lactamase gene is located on the bacterial chromosome, with no mobile genetic elements such as transposons or integrons present nearby, suggesting a low probability of horizontal gene transfer. This study provides a solid foundation for the safety evaluation of Akkermansia and is significant for monitoring antibiotic resistance genes derived from probiotics.
The International Journal of Food Microbiology is an international journal that features comprehensive research on engineering technology and food science. It is classified as a top journal among the Tier 1 in Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. The journal was founded in 1984 by Elsevier to promote and disseminate research findings in both basic and applied food microbiology, having a significant impact in this field.
Source: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110998